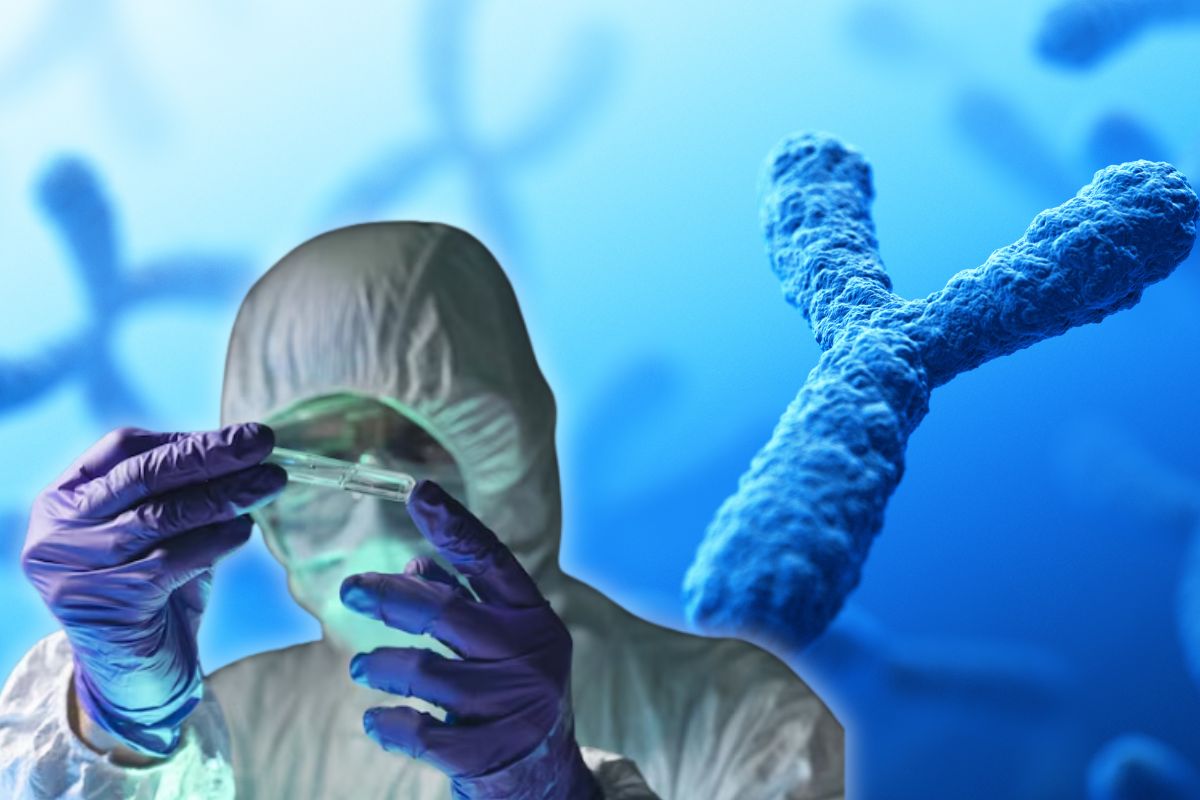
Crucially important for male sex in humans, the Y chromosome is gradually but steadily declining. Both scientists and the general people have become quite interested in and concerned about these phenomena. Over millions of years, the Y chromosome—which contains the SRY gene sparking masculine development—has been shedding genes. This blog explores the subtleties of this genetic decline, its consequences, and the possible direction human reproduction could go.
Table of Contents
ToggleIn humans, the Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes; the X chromosome is the other. Whereas women have two X chromosomes (XX), men usually have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). Fewer genes and a much smaller size than the X chromosome define the Y chromosome. Though it is little, it is very important for male growth.
On the Y chromosome, the SRY gene sets off the development of testes, which in turn generates male hormones guiding the development of male physical traits.
The Y chromosome has lost a great lot of its genes over the previous three hundred million years. It contained around 1,438 genes originally, but only 45 now. The particular manner the Y chromosome is passed on accounts for this loss.
The Y chromosome is passed on essentially unaltered from father to son unlike other chromosomes, which recombine and exchange genetic material during reproduction. Harmful mutations build up over time due to lack of recombination, therefore causing gene loss.
Scientists project that the Y chromosome may vanish totally within the next 11 million years at the present pace of gene loss1. This possibility begs issues regarding the direction of human reproduction and male development going forward. The SRY gene would be lost without the Y chromosome, therefore maybe causing the extinction of men as we know them.
Fascinatingly, several animals have already lost their Y chromosomes and evolved other sex-determining systems. For instance, a native rodent species from Japan, the spiny rat has developed a new male-determining gene on another chromosome1.
This adaptability implies that humans may develop new methods to identify sex and guarantee reproduction even if the Y chromosome vanished.
Human reproduction suffers major consequences from the Y chromosome possibly disappearing. Should men vanish, the dynamics of human numbers would be drastically changed. Still, there is optimism given the development of fresh sex-determining systems seen in other animals. Scientists are looking at the prospect of spotting and using substitute genes to replace the SRY gene.
Understanding the direction of human reproduction depends on a constant study of the Y chromosome and its drop. Studying creatures without their Y chromosomes can help researchers understand possible human evolutionary paths. Moreover, developments in reproductive technology and genetic engineering might provide means to lessen the consequences of Y chromosome loss.
Also, read Exprohelp – Your Comprehensive Healthcare Partner
Moreover, the possible removal of the Y chromosome raises moral and societal issues. Without conventional male and female roles, how will society adjust? How may this affect relationships and gender identification? These problems underline the necessity of a multidisciplinary approach to investigate the drop in the Y chromosome including viewpoints from ethics, society, and biology.
A fascinating and complicated phenomenon with far-reaching consequences is the progressive loss of the Y chromosome. Though the possible extinction of men as we know them raises questions, life’s adaptation gives hope.
Examining various animals and developing genetic research can help us to investigate fresh approaches to guarantee ongoing human reproduction. Unexpected answers in the future will show the resiliency and inventiveness of life on Earth.