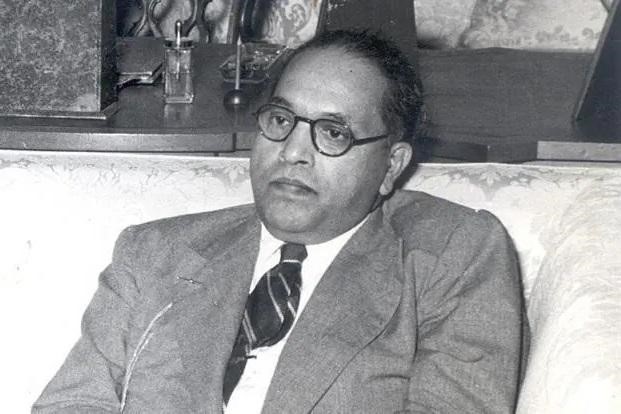
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, a towering figure in Indian history, was not just a scholar and statesman but also a relentless crusader for social justice. Born into a Dalit family in 1891, he faced the harsh realities of caste discrimination from a young age. Despite these obstacles, he pursued education with determination, earning multiple degrees including a doctorate from Columbia University. His early experiences deeply influenced his views on social justice and equality.
Table of Contents
ToggleGrowing up in a society deeply divided by caste, Ambedkar faced discrimination at every turn. Denied access to water sources and schools, he experienced firsthand the injustices of the caste system. However, he refused to be defined by his circumstances and dedicated himself to his studies. His academic achievements opened doors for him to study abroad, where he was exposed to different ideas and philosophies that shaped his own views.
Quests of ambedkar on social justice became intertwined with India’s struggle for independence. He realized that political freedom alone was not enough; true liberation required the eradication of social inequalities. He emerged as a prominent voice advocating for the rights of Dalits and other marginalized communities, challenging both British colonial rule and the entrenched caste system.
At the heart of Ambedkar’s philosophy was the belief in the inherent dignity of every individual, regardless of their caste or social status. Ambedkar on social justice, as the cornerstone of a democratic society, where every person has equal rights and opportunities. His vision went beyond mere legal equality to encompass a fundamental restructuring of society based on principles of fairness and inclusivity.
Ambedkar saw the caste system as a social evil that perpetuated inequality and denied basic human rights to millions. He led movements to open up public places and temples to all castes, challenging the deeply ingrained practice of untouchability. His efforts laid the foundation for the legal abolition of untouchability in independent India.
In his seminal work, “Annihilation of Caste,” Ambedkar called for a radical rethinking of India’s social structure. He argued that the caste system was not just a division of labor but a system of graded inequality that dehumanized millions. He called on Indians to renounce their caste identities and embrace a new social order based on equality and fraternity.
As independent India’s first Law Minister, Ambedkar played a key role in drafting the Indian Constitution. He ensured that it enshrined principles of equality, justice, and fraternity, laying the foundation for a democratic and inclusive society. He also championed legal reforms that aimed to uplift the marginalized and protect their rights.
Ambedkar’s political career was marked by his efforts to give voice to the voiceless. He founded the Republican Party of India to represent the interests of Dalits and other oppressed groups. Despite facing many challenges and setbacks, he remained steadfast in his commitment to social justice until his death in 1956.
Ambedkar’s legacy is profound and enduring. His tireless efforts paved the way for the empowerment of Dalits and other marginalized communities. Ideas of Ambedkar on social justice movements in India and around the world, remind us of the ongoing struggle for equality and dignity.
Today, Dr. B.R. Ambedkar is revered as the architect of the Indian Constitution and a champion of social justice. His life and work serve as a beacon of hope for millions, inspiring them to fight against discrimination and injustice. His message of equality and fraternity remains as relevant today as it was during his lifetime, reminding us of our shared humanity and the need to strive for a more just and inclusive society.
Ambedkar’s main contributions include his efforts to abolish untouchability, his advocacy for equal rights for all citizens, and his role in drafting the Indian Constitution.
Experiences of discrimination and social exclusion as a Dalit shaped views of ambedkar on social justice and drove his efforts to achieve equality for all.
Ambedkar’s “Annihilation of Caste” speech is significant because it critiqued the caste system and called for its complete abolition, challenging prevailing social norms.
Ambedkar’s legal reforms aimed to uplift marginalized communities and protect their rights, laying the foundation for a more inclusive and just society.
Today, Ambedkar’s legacy lives on in the ongoing struggle for social justice and equality, inspiring movements and individuals to continue his work.
Experiences deeply influenced Ambedkar on social justice, leading him to dedicate his life to fighting for the rights of marginalized communities.
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar’s legacy in modern India is profound, his role in drafting the Indian Constitution and advocating for the rights of minorities and other marginalized communities has earned him a revered place in Indian history.